BMGD Workflows Guide
Complete reference for all BMGD workflows organized by development phase.
Workflow Overview
Section titled “Workflow Overview”BMGD workflows are organized into four phases:
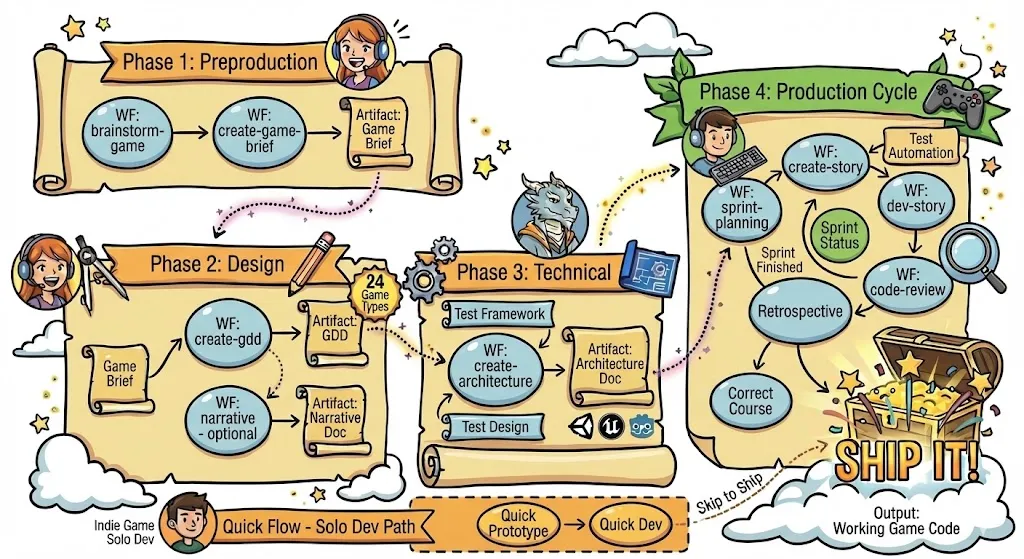
Phase 1: Preproduction
Section titled “Phase 1: Preproduction”Brainstorm Game
Section titled “Brainstorm Game”Command: brainstorm-game
Agent: Game Designer
Input: None required
Output: Ideas and concepts (optionally saved)
Description: Guided ideation session using game-specific brainstorming techniques:
- MDA Framework - Mechanics → Dynamics → Aesthetics analysis
- Core Loop Workshop - Define the fundamental gameplay loop
- Player Fantasy Mining - Explore what players want to feel
- Genre Mashup - Combine genres for unique concepts
Steps:
- Initialize brainstorm session
- Load game-specific techniques
- Execute ideation with selected techniques
- Summarize and (optionally) hand off to Game Brief
Game Brief
Section titled “Game Brief”Command: create-game-brief
Agent: Game Designer
Input: Ideas from brainstorming (optional)
Output: {output_folder}/game-brief.md
Description: Captures your game’s core vision and fundamentals. This is the foundation for all subsequent design work.
Sections covered:
- Game concept and vision
- Design pillars (3-5 core principles)
- Target audience and market
- Platform considerations
- Core gameplay loop
- Initial scope definition
Phase 2: Design
Section titled “Phase 2: Design”GDD (Game Design Document)
Section titled “GDD (Game Design Document)”Command: create-gdd
Agent: Game Designer
Input: Game Brief
Output: {output_folder}/gdd.md (or sharded into {output_folder}/gdd/)
Description: Comprehensive game design document with genre-specific sections based on 24 supported game types.
Core sections:
- Executive Summary
- Gameplay Systems
- Core Mechanics
- Progression Systems
- UI/UX Design
- Audio Design
- Art Direction
- Technical Requirements
- Game-Type-Specific Sections
- Epic Generation (for sprint planning)
Features:
- Game type selection with specialized sections
- Hybrid game type support
- Automatic epic generation
- Scale-adaptive complexity
Narrative Design
Section titled “Narrative Design”Command: narrative
Agent: Game Designer
Input: GDD (required), Game Brief (optional)
Output: {output_folder}/narrative-design.md
Description: For story-driven games. Creates comprehensive narrative documentation.
Sections covered:
- Story Foundation (premise, themes, tone)
- Story Structure (acts, beats, pacing)
- Characters (protagonists, antagonists, supporting, arcs)
- World Building (setting, history, factions, locations)
- Dialogue Framework (style, branching)
- Environmental Storytelling
- Narrative Delivery Methods
- Gameplay-Narrative Integration
- Production Planning (scope, localization, voice acting)
- Appendices (relationship map, timeline)
Narrative Complexity Levels:
- Critical - Story IS the game (visual novels, adventure games)
- Heavy - Deep narrative with gameplay (RPGs, story-driven action)
- Moderate - Meaningful story supporting gameplay
- Light - Minimal story, gameplay-focused
Phase 3: Technical
Section titled “Phase 3: Technical”Game Architecture
Section titled “Game Architecture”Command: create-architecture
Agent: Game Architect
Input: GDD, Narrative Design (optional)
Output: {output_folder}/game-architecture.md
Description: Technical architecture document covering engine selection, system design, and implementation approach.
Sections covered:
- Executive Summary
- Engine/Framework Selection
- Core Systems Architecture
- Data Architecture
- Performance Requirements
- Platform-Specific Considerations
- Development Environment
- Testing Strategy
- Build and Deployment
- Technical Risks and Mitigations
Phase 4: Production
Section titled “Phase 4: Production”Production workflows inherit from BMM and add game-specific overrides.
Sprint Planning
Section titled “Sprint Planning”Command: sprint-planning
Agent: Game Scrum Master
Input: GDD with epics
Output: {implementation_artifacts}/sprint-status.yaml
Description: Generates or updates sprint tracking from epic files. Sets up the sprint backlog and tracking.
Sprint Status
Section titled “Sprint Status”Command: sprint-status
Agent: Game Scrum Master
Input: sprint-status.yaml
Output: Sprint summary, risks, next action recommendation
Description: Summarizes sprint progress, surfaces risks (stale file, orphaned stories, stories in review), and recommends the next workflow to run. Supports three modes:
- interactive (default): Displays summary with menu options
- validate: Checks sprint-status.yaml structure
- data: Returns raw data for other workflows
Create Story
Section titled “Create Story”Command: create-story
Agent: Game Scrum Master
Input: GDD, Architecture, Epic context
Output: {output_folder}/epics/{epic-name}/stories/{story-name}.md
Description: Creates implementable story drafts with acceptance criteria, tasks, and technical notes. Stories are marked ready-for-dev directly when created.
Validation: validate-create-story
Dev Story
Section titled “Dev Story”Command: dev-story
Agent: Game Developer
Input: Story (ready for dev)
Output: Implemented code
Description: Implements story tasks following acceptance criteria. Uses TDD approach (red-green-refactor). Updates sprint-status.yaml automatically on completion.
Code Review
Section titled “Code Review”Command: code-review
Agent: Game Developer
Input: Story (ready for review)
Output: Review feedback, approved/needs changes
Description: Thorough QA code review with game-specific considerations (performance, 60fps, etc.).
Retrospective
Section titled “Retrospective”Command: epic-retrospective
Agent: Game Scrum Master
Input: Completed epic
Output: Retrospective document
Description: Facilitates team retrospective after epic completion. Captures learnings and improvements.
Correct Course
Section titled “Correct Course”Command: correct-course
Agent: Game Scrum Master or Game Architect
Input: Current project state
Output: Correction plan
Description: Navigates significant changes when implementation is off-track. Analyzes impact and recommends adjustments.
Workflow Status
Section titled “Workflow Status”Command: workflow-status
Agent: All agents
Output: Project status summary
Description: Checks current project status across all phases. Shows completed documents, current phase, and next steps.
Quick-Flow Workflows
Section titled “Quick-Flow Workflows”Fast-track workflows that skip full planning phases. See Quick-Flow Guide for detailed usage.
Quick-Prototype
Section titled “Quick-Prototype”Command: quick-prototype
Agent: Game Designer, Game Developer
Input: Idea or concept to test
Output: Working prototype, playtest results
Description: Rapid prototyping workflow for testing game mechanics and ideas quickly. Focuses on “feel” over polish.
Use when:
- Testing if a mechanic is fun
- Proving a concept before committing to design
- Experimenting with gameplay ideas
Quick-Dev
Section titled “Quick-Dev”Command: quick-dev
Agent: Game Developer
Input: Tech-spec, prototype, or direct instructions
Output: Implemented feature
Description: Flexible development workflow with game-specific considerations (performance, feel, integration).
Use when:
- Implementing features from tech-specs
- Building on successful prototypes
- Making changes that don’t need full story workflow
Quality Assurance Workflows
Section titled “Quality Assurance Workflows”Game testing workflows for automated testing, playtesting, and quality assurance across Unity, Unreal, and Godot.
Test Framework
Section titled “Test Framework”Command: test-framework
Agent: Game QA
Input: Game project
Output: Configured test framework
Description: Initialize a production-ready test framework for your game engine:
- Unity: Unity Test Framework with Edit Mode and Play Mode tests
- Unreal: Unreal Automation system with functional tests
- Godot: GUT (Godot Unit Test) framework
Creates:
- Test directory structure
- Framework configuration
- Sample unit and integration tests
- Test documentation
Test Design
Section titled “Test Design”Command: test-design
Agent: Game QA
Input: GDD, Architecture
Output: {output_folder}/game-test-design.md
Description: Creates comprehensive test scenarios covering:
- Core gameplay mechanics
- Progression and save systems
- Multiplayer (if applicable)
- Platform certification requirements
Uses GIVEN/WHEN/THEN format with priority levels (P0-P3).
Automate
Section titled “Automate”Command: automate
Agent: Game QA
Input: Test design, game code
Output: Automated test files
Description: Generates engine-appropriate automated tests:
- Unit tests for pure logic
- Integration tests for system interactions
- Smoke tests for critical path validation
Playtest Plan
Section titled “Playtest Plan”Command: playtest-plan
Agent: Game QA
Input: Build, test objectives
Output: {output_folder}/playtest-plan.md
Description: Creates structured playtesting sessions:
- Session structure (pre/during/post)
- Observation guides
- Interview questions
- Analysis templates
Playtest Types:
- Internal (team validation)
- External (unbiased feedback)
- Focused (specific feature testing)
Performance Test
Section titled “Performance Test”Command: performance-test
Agent: Game QA
Input: Platform targets
Output: {output_folder}/performance-test-plan.md
Description: Designs performance testing strategy:
- Frame rate targets per platform
- Memory budgets
- Loading time requirements
- Benchmark scenarios
- Profiling methodology
Test Review
Section titled “Test Review”Command: test-review
Agent: Game QA
Input: Existing test suite
Output: {output_folder}/test-review-report.md
Description: Reviews test quality and coverage:
- Test suite metrics
- Quality assessment
- Coverage gaps
- Recommendations
Utility Workflows
Section titled “Utility Workflows”Party Mode
Section titled “Party Mode”Command: party-mode
Agent: All agents
Description: Brings multiple agents together for collaborative discussion on complex decisions.
Advanced Elicitation
Section titled “Advanced Elicitation”Command: advanced-elicitation
Agent: All agents (web only)
Description: Deep exploration techniques to challenge assumptions and surface hidden requirements.
Standalone BMGD Workflows
Section titled “Standalone BMGD Workflows”BMGD Phase 4 workflows are standalone implementations tailored for game development:
workflow: '{project-root}/_bmad/bmgd/workflows/4-production/dev-story/workflow.yaml'This means:
- BMGD workflows are self-contained with game-specific logic
- Game-focused templates, checklists, and instructions
- No dependency on BMM workflow files
Next Steps
Section titled “Next Steps”- Quick Start Guide - Get started with BMGD
- Quick-Flow Guide - Rapid prototyping and development
- Agents Guide - Agent reference
- Game Types Guide - Game type templates